|
|
Overview: Reference Browser |
|
|
Overview: Reference Browser |
The Reference Browser displays context material pertaining to a segment. This information is displayed as the user selects that segment - giving more context, thus ensuring a better quality translation. An internet browser is used to display the content, so a wide variety of reference formats is supported. Images, audio, video and documentation formats, for example, could be used as references for a segment.
|
|
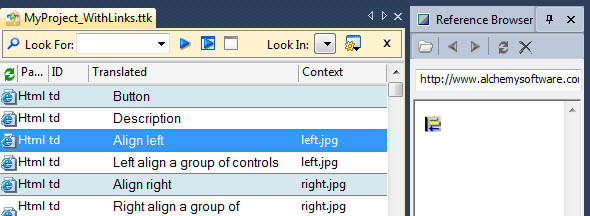
Context Links are links to external files. They are not embedded within a Project TTK. |
This example shows 'Align Left' as the selected segment in the workspace and the associated image appearing in the Reference Browser on the right - this is giving the indication that this is for aligning controls in user-interface screen. This additional knowledge assists in ensuring the most appropriate translation is provided.a
Press the automatic refresh button ![]() so it remains selected. In this mode the Reference Browser is refreshed with context links every time a segment is selected.
so it remains selected. In this mode the Reference Browser is refreshed with context links every time a segment is selected.
If automatic refresh is not enabled, you can refresh the reference browser on-demand using the Refresh button ![]()
|
|
Always add context links from the Reference Root. If you have a lot of images, build a folder structure in your ReferenceRoot for maintaining the links. To transfer images between machines, simply copy the ReferenceRoot folder structure to the other machine. All context links will remain active. |
Adding a Context Link
|
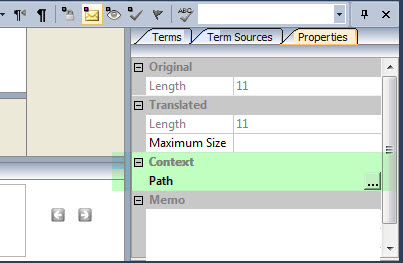 |
Online references are stored as entire URLs. Using online URLs is very powerful as they are available to anyone who opens the project file without having to transfer the image files along with a project TTK.
Context Links can be added in batch using xliff. The industry standard xliff format has structures for storing context information. If context information of type x-reference is present, CATALYST will place the value in the Path field for the Context property. Using this mechanism, Context Links for many segments can be applied on insertion. The following image shows the syntax for storing the context path.
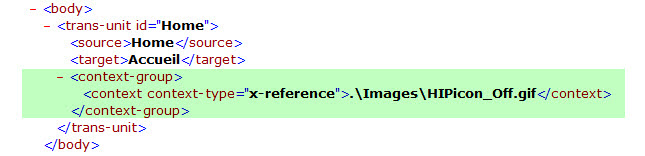
The path to local files are stored as relative paths. To make portability easier, they are always stored as paths relative to the Reference Root. This means that if a Project TTK is moved, the images do not need to be moved. The location of the TTK has no bearing on the location of the image.
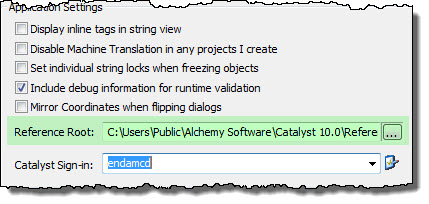
The Reference Root is a CATALYST setting that is configurable via the Tools - Options - Application screen. The default path is in your Public folder, i.e. \Public\Alchemy Software\Catalyst 10.0\ReferenceRoot\
You should build up your context links in this area, or change the location for the ReferenceRoot and build your image structure at that location.
If a URL is present as a context link, CATALYST will try to connect to the internet to display the referenced image.
If a file path is present as the context link, CATALYST will resolve the path relative to the Reference Root to locate the image. If this resolves to a path, that file is displayed in the Reference Browser. If no file is found at that location, a message is displayed to the user indicating that the file could not be located.
If the Reference Root is set to the default "C:\Users\Public\Alchemy Software\Catalyst 10.0\Reference Root\"
... and a context link is set to "ScreenShot.jpg"
... the reference browser will resolve the path as
"C:\Users\Public\Alchemy Software\Catalyst 10.0\Reference Root\ScreenShot.jpg"
If the Reference Root is changed to "C:\MyProject\images\"
...and the context link is set as ".\Project1\ScreenShot.jpg"
...the reference browser will resolve the path as
"C:\MyProject\images\Project1\ScreenShot.jpg"